How does it work
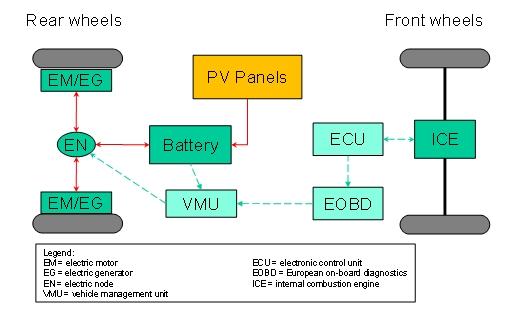
The above figure shows a block diagram
of the mild hybrid solar vehicle.
The hybridizing equipment is installed
on a conventional car (two front wheels drive),
in which the front wheels are propelled by the
Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) controlled by an Engine Control
Unit (ECU). The vehicle is also equipped with an EOBD gate (On
Board Diagnostics protocol), which allows accessing data such
as pedal position, vehicle speed, engine speed, manifold pressure
and other variables.
A mild parallel hybrid structure
is obtained by substituting/integrating the rear wheels
with in-wheel motors. In that way, the vehicle
can operate in pure electric mode (when ICE is
switched off or disconnected by the front wheels) or in hybrid
mode (when the ICE drives the front wheels and the rear
in-wheel motors operate in traction mode or in generation mode,
corresponding to a positive or negative torque). The battery can
be recharged both by rear wheels, when operating in generation
mode, and by photovoltaic panels. The Vehicle
Management Unit (VMU), which is part of the invention
and implements control logics compatible with typical
drive styles of conventional-car users, receives the
data from OBD gate, from battery (SOC estimation)
and drives in-wheel motors by properly acting on the electric
node EN. A display on the dashboard may advice the driver about
the actual operation of the system.
The Kit
The kit of equipments, to be installed
for converting a conventional car into a hybrid solar vehicle,
will include:
-
A couple of in-wheel motors,
which can be purchased (they are currently commercialized by
Michelin and other manufacturers) and eventually modified according
to system requirements.
-
An auxiliary battery pack, presumably
consisting of Lithium-Ion cells.
-
An additional control system
(VMU), which is conceived to be self-adaptive enough to be suitable
for different vehicle and in-wheel typologies and features.
-
A connector for the OBD gate
along with related cables, to be connected to the VMU.
-
Either a flexible or semi-rigid
solar panel, to be installed on vehicle roof.
-
Possibly, a small additional
display to be placed on car instrument panel, which could include
a state of charge indicator for the auxiliary battery along
with additional control buttons to switch from one operating
mode to another .